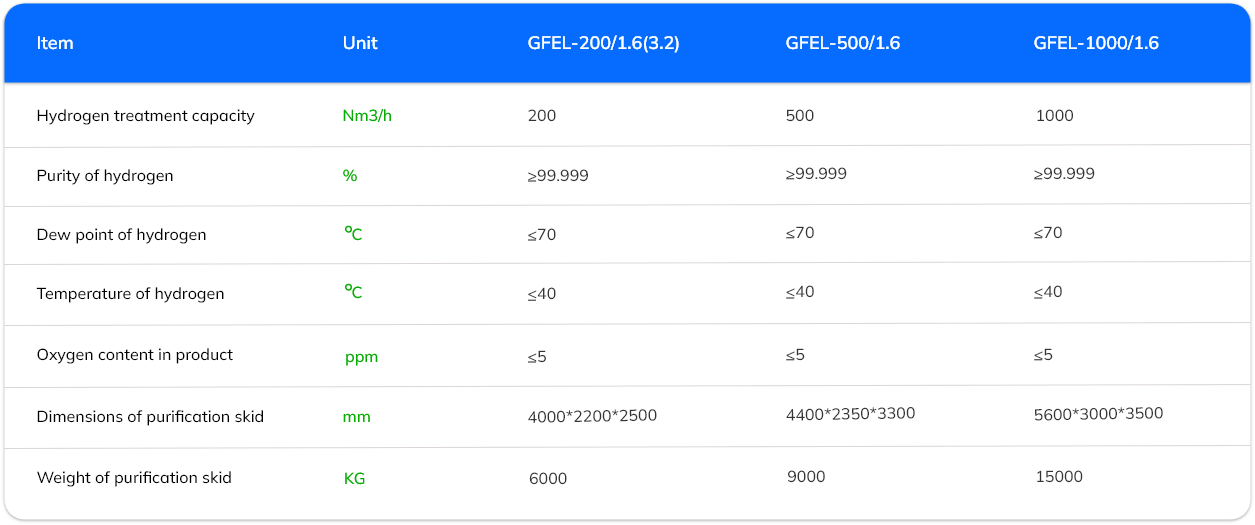
Hydrogen Generation System
The Hydrogen Generation system consists of alkaline water electrolysis (AWE) electrolysers, a gas-liquid separator, a purification
unit, and an auxiliary system. Each single-stack setup can achieve a capacity of up to 1000 Nm³/h (5 MW).
unit, and an auxiliary system. Each single-stack setup can achieve a capacity of up to 1000 Nm³/h (5 MW).

HyCee’s Hydrogen Generation System offers flexible, high-efficiency hydrogen production using both Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) and Alkaline Water Electrolysis (AWE) technologies. Designed to suit a range of operational needs, our systems deliver clean hydrogen for mobility, industrial use, or energy storage. PEM electrolysers provide fast response and high purity, ideal for dynamic loads and compact setups. AWE systems offer proven, cost-effective performance for larger-scale or continuous operations. Each unit is engineered with durability, safety, and efficiency at its core, and can be integrated with renewable energy sources for zero-emission output.
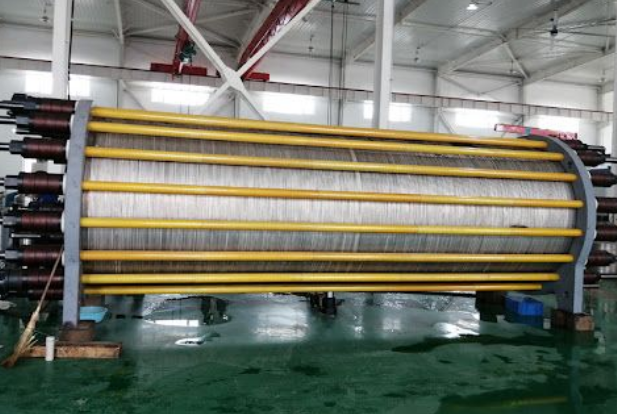
Electrolysis Stack
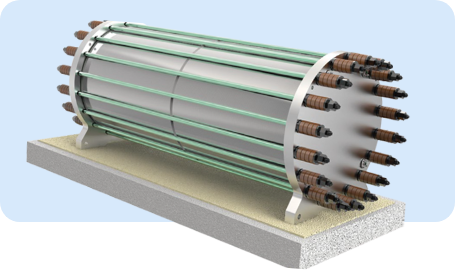
The electrolysis stack functions at a pressure of either 1.6 Mpa or 3.2 Mpa, depending on system configuration. This alkaline electrolysis system is known for its high hydrogen output, exceptional purity, long operational lifespan, and consistent performance. It also stands out for its low maintenance needs and straightforward operation, making it a reliable choice for continuous hydrogen production.
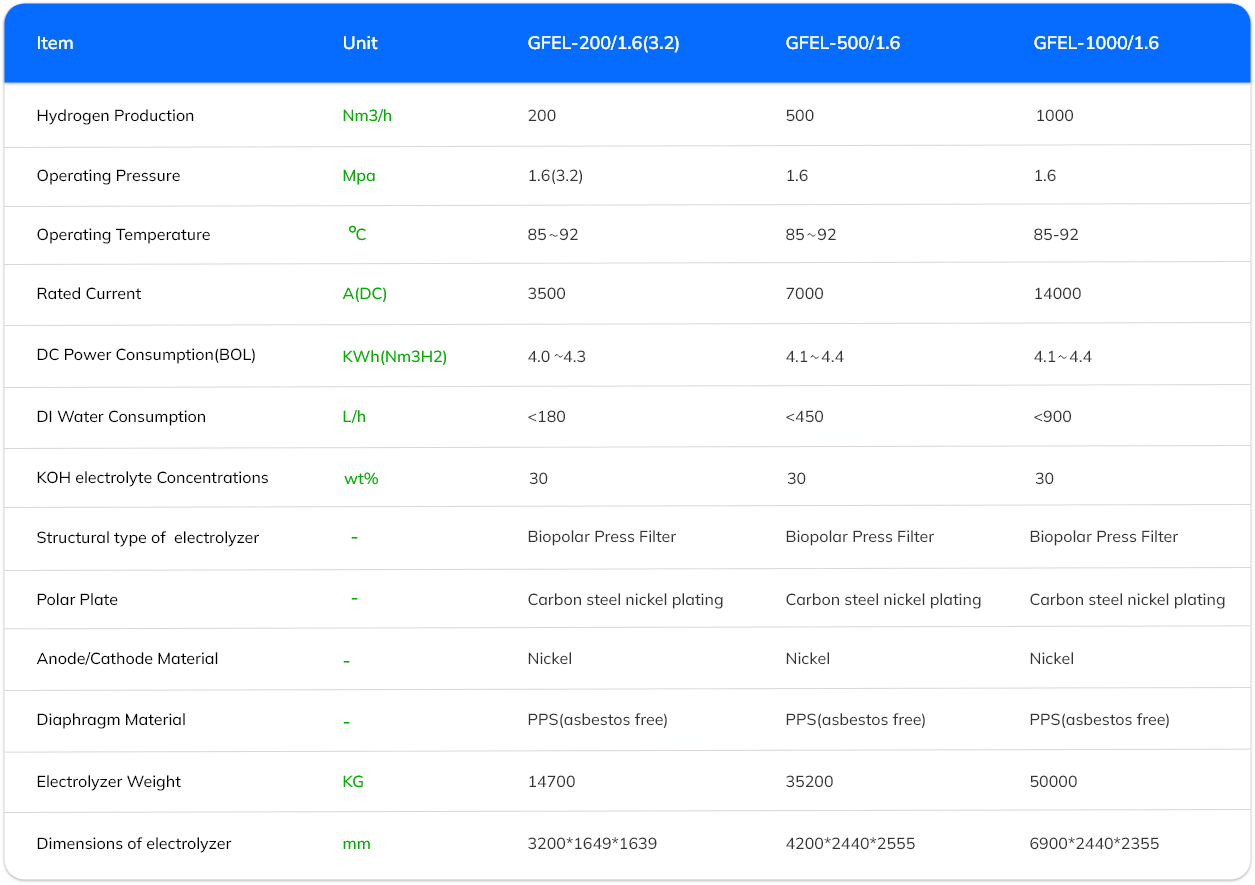
Gas Seperation
System

Hydrogen and oxygen exit the electrolyser via their respective convergence channels along with lye, and flow into the gas separator. Relying on gravity, the hydrogen (or oxygen) is separated from the lye as they settle. The isolated hydrogen (or oxygen) is discharged from the top section of the separator and directed to the hydrogen (or oxygen) heat exchanger for cooling. Any remaining liquid droplets are extracted at the top of the separator through the hydrogen washing separator. Finally, the hydrogen passes through a regulating valve before being delivered downstream.
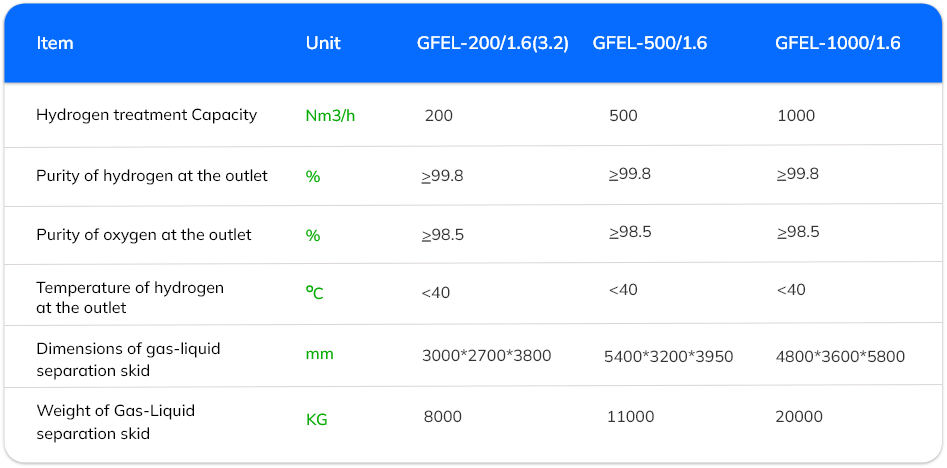
Hydrogen Purification
System
Hydrogen produced via water electrolysis typically contains traces of oxygen impurities and saturated moisture. To purify it, a de-aerator uses a catalyst reaction to convert residual oxygen into water, while a molecular sieve in the dryer removes remaining moisture from the hydrogen stream. After this treatment, the oxygen content is reduced to 5 ppm or lower, and the hydrogen purity reaches 99.999%.